Okay, buckle up buttercup, because we’re diving headfirst into a seriously hefty topic: the connection between climate change & the global economic crisis. It’s not just some abstract environmental issue anymore, folks; it’s hitting our wallets harder than a surprise tax bill!. The two are inextricably linked, like peanut butter & jelly, or a stubborn stain on a white shirt. Ignoring one means ignoring the other, & that’s a recipe for disaster of epic proportions!
Think about it. Extreme weather events – hurricanes that cripple infrastructure, droughts that decimate crops, floods that displace millions – aren’t just environmental tragedies, they’re economic ones too. The cost of rebuilding after a superstorm? Astronomical! The losses in agricultural production due to prolonged droughts? Mind-boggling! The ripple effects on global supply chains? Absolutely devastating!. We’re talking billions, if not trillions, of dollars in damages annually, folks; that’s money that could be used for…well, almost anything more productive than disaster relief, right?.
And it’s not just the immediate, catastrophic events that drain our resources. The slow, creeping effects of climate change are just as insidious, economically speaking. Rising sea levels threaten coastal communities & vital infrastructure, forcing costly relocation & protection measures. Changes in precipitation patterns impact agricultural yields, leading to food shortages & price hikes, making life difficult for those who already struggle. Heatwaves reduce worker productivity & drive up healthcare costs; can’t focus in the scorching sun! Heat is really the enemy! Extreme weather also makes it challenging to perform daily activities like school and commuting making us feel increasingly depressed as this is a crisis we don’t see a solution for just yet!.
Furthermore, the transition to a low-carbon economy, while crucial for mitigating climate change, presents its own set of economic challenges. Investing in renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, & developing sustainable technologies requires significant upfront investment. While this transition presents enormous opportunities for innovation & economic growth – green jobs, anyone? – it also demands a fundamental shift in our economic systems, requiring adaptation and preparedness which many find incredibly scary and uncertain!.
Ultimately, ignoring the link between climate change & the global economic crisis is not only irresponsible but also incredibly costly. The longer we wait to take meaningful action, the more expensive & disruptive the consequences will be, exacerbating inequality and threatening to push the worlds’ poor and destitute into unbearable levels of suffering and starvation. This isn’t about saving the planet for future generations; it’s about protecting our present economic stability & ensuring a sustainable future for everyone – every single person on the planet! Now that’s something we all agree on, isn’t it?! Let’s start talking solutions!.
Related Post : The Global Energy Crisis: What’s Behind the Rising Energy Prices?
The Deepening Connection Between Climate Change and the Global Economic Crisis
The relationship between Climate Change and the global economy is no longer subtle; it’s a deeply intertwined crisis. We’re witnessing a dangerous nexus where environmental degradation fuels economic instability, creating a vicious cycle with far-reaching consequences. Understanding this connection is crucial for navigating the challenges ahead and building a more sustainable future.
Understanding the Climate Change-Economic Crisis Nexus
What is the link between climate change and economic instability? The link is multifaceted. Climate change acts as a “threat multiplier,” exacerbating existing economic vulnerabilities and creating new ones. Extreme weather events, resource scarcity, and mass migration all directly impact economic productivity, stability, and growth. It’s a complex interplay within the field of Climate Economics, requiring sophisticated analysis to fully grasp its implications.
How does climate change directly impact economic sectors (agriculture, tourism, etc.)? Agriculture, a cornerstone of many economies, is highly susceptible to changes in temperature and rainfall patterns. Droughts, floods, and extreme heat reduce crop yields, driving up food prices and impacting food security. Similarly, the tourism sector, reliant on stable weather conditions and pristine environments, suffers from extreme weather events and environmental degradation. These are just two examples of how climate change directly undermines economic sectors, leading to job losses and reduced economic output.
Examples of climate-related economic disasters (hurricanes, droughts, floods) and their costs. Consider Hurricane Katrina in 2005, causing billions of dollars in damage and long-term economic disruption. The 2011 drought in East Africa led to widespread famine and economic hardship. The 2017 Atlantic hurricane season resulted in unprecedented devastation across the Caribbean and the United States. These events highlight the enormous economic costs associated with climate-related disasters, costs that are likely to increase significantly in the coming years.
The role of climate change in creating resource scarcity (water, food) and price volatility. Climate change intensifies existing resource scarcity, particularly water and food. Reduced rainfall and increased evaporation lead to water shortages, impacting agriculture, industry, and domestic consumption. Decreased crop yields and disruptions to food supply chains contribute to price volatility, disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations.
The Global Impact of Climate Change on the Economy
Climate change and global supply chains: disruptions and vulnerabilities. Global supply chains are intricately interconnected, making them highly vulnerable to climate-related disruptions. Extreme weather events can halt transportation, damage infrastructure, and disrupt production, leading to shortages and price increases. This vulnerability underscores the need for climate-resilient supply chains.
How climate migration and displacement affect economies globally. Climate change is a major driver of migration and displacement, as people flee areas impacted by extreme weather events, sea-level rise, and resource scarcity. This mass migration places significant strain on receiving countries, impacting infrastructure, social services, and labor markets.
The uneven distribution of climate change impacts: who bears the brunt economically? The economic impacts of climate change are not evenly distributed. Developing countries and vulnerable populations are disproportionately affected, lacking the resources to adapt and cope with climate-related shocks. This economic inequality exacerbates existing social injustices.
Climate change and national security: economic implications of instability. Climate change can destabilize nations, leading to conflicts over resources, mass migration, and increased security threats. This instability has significant economic implications, impacting investment, trade, and overall economic growth.
Climate Economics: Cost of Inaction vs. Investment
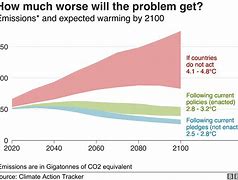
Assessing the economic costs of climate change inaction (future damages). The economic costs of inaction on climate change are far greater than the costs of taking action. Failing to mitigate climate change will result in significantly higher future damages from extreme weather events, resource scarcity, and other climate-related impacts.
The economic benefits of climate action (green jobs, renewable energy). Investing in climate action offers significant economic benefits. The transition to a green economy creates new jobs in renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable infrastructure. This transition also fosters innovation and technological advancement.
Financing the transition to a green economy: challenges and opportunities. Financing the transition to a green economy presents significant challenges, requiring substantial investments from governments, the private sector, and international organizations. However, there are also significant opportunities for investment in green technologies and sustainable infrastructure.
Investing in climate resilience: protecting economies from future shocks. Investing in climate resilience measures—such as improved infrastructure, early warning systems, and disaster preparedness—can significantly reduce the economic costs of future climate-related shocks.
Climate Change, Economic Crisis, and Global Policy
The role of international agreements (Paris Agreement) in addressing climate economics. International agreements like the Paris Agreement are crucial for coordinating global efforts to mitigate climate change and address its economic impacts. These agreements provide a framework for cooperation and collaboration among nations.
Government policies and economic incentives for climate action. Government policies play a vital role in driving climate action through economic incentives such as carbon pricing, subsidies for renewable energy, and investments in green infrastructure.
The private sector’s role in driving climate-friendly investments. The private sector has a crucial role to play in driving climate-friendly investments, developing and deploying green technologies, and promoting sustainable business practices.
Consumer behavior and its impact on the climate and the economy. Consumer behavior significantly influences the climate and the economy. Sustainable consumption patterns, such as reducing waste and choosing environmentally friendly products, can contribute to a more sustainable economy.
Mitigating the Climate Change-Economic Crisis Link
Strategies for adapting to the economic impacts of climate change. Adapting to the economic impacts of climate change requires strategies to improve resilience, including investing in climate-resilient infrastructure, diversifying economies, and strengthening social safety nets.
Building climate resilience in vulnerable economies. Building climate resilience in vulnerable economies is crucial for reducing their vulnerability to climate-related shocks and fostering sustainable economic growth.
Investing in renewable energy and sustainable infrastructure. Investing in renewable energy and sustainable infrastructure is essential for mitigating climate change and creating a more sustainable and resilient economy.
Promoting sustainable consumption and production patterns. Promoting sustainable consumption and production patterns can significantly reduce the environmental impact of economic activity and contribute to a more sustainable economy.
Climate Change: A Looming Economic Threat?
Future scenarios: potential economic impacts of continued inaction. Continued inaction on climate change will lead to increasingly severe economic consequences, including widespread displacement, resource conflicts, and significant disruptions to global supply chains.
The urgency of addressing climate change for economic stability. Addressing climate change is not just an environmental imperative; it’s also an economic necessity. Failure to act will undermine economic stability and prosperity.
Exploring technological innovations for climate mitigation and adaptation. Technological innovation is crucial for both mitigating and adapting to climate change. This includes developing renewable energy technologies, improving energy efficiency, and creating climate-resilient infrastructure.
The importance of international cooperation in addressing climate economics. International cooperation is essential for effectively addressing the economic challenges posed by climate change. This includes sharing knowledge, technology, and resources.
Conclusion: A Path Towards Sustainable Economic Growth
The connection between Climate Change and the global economic crisis is undeniable. Addressing this intertwined crisis requires a comprehensive and coordinated approach, encompassing mitigation, adaptation, and international cooperation. The path towards sustainable economic growth necessitates a fundamental shift towards a green economy, one that prioritizes environmental sustainability and social equity. The cost of inaction far outweighs the cost of decisive action. The time for bold and transformative change is now.
